Specification of Rotatable Sphincterotome
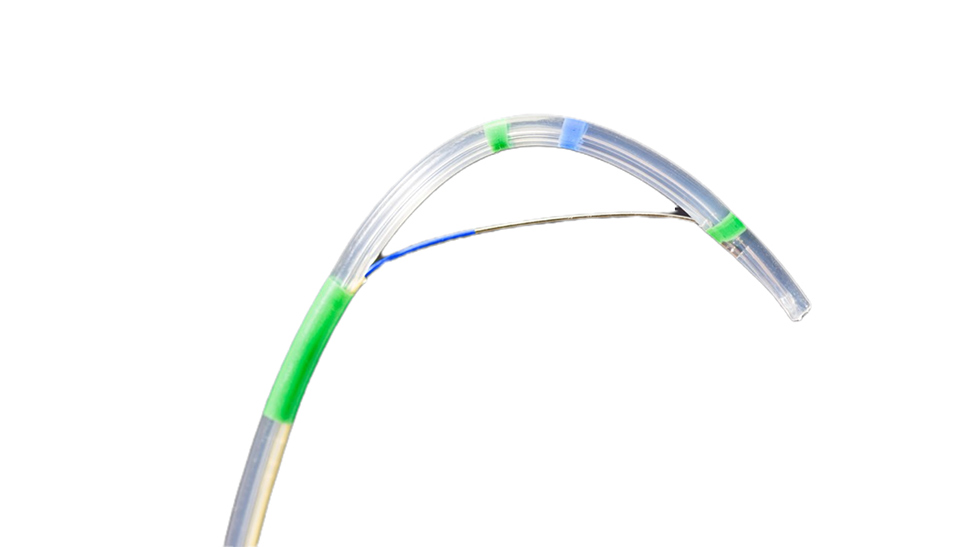
Rotatable Sphincterotome
REF
standard | Structure | Tip Length
(mm) | Cutting Length
(mm) | Working Length
| Compatible Guidewire | Minimum Working Channel (mm) | Unit/Box |
| RST0425N | 3-lumen | 4 | 25 | 1900 | 0.035” | 2.8 | 1 |
| RST0430N | 3-lumen | 4 | 30 |
| RST0725N | 3-lumen | 7 | 25 |
| RST0730N | 3-lumen | 7 | 30 |
Rotatable Sphincterotome (Preassembled with Guidewire)
| REF | Structure | Catheter | Tip Length
(mm) | Cutting wire Length
(mm) | Minimum Working Channel (mm) | Guide Wire | Unit/Box |
| Standard | Outer Diam.
(mm) | Length
(mm) | Diam. (inch) | Length (mm) | Tip Shape | Hardness |
| RST0425NGW0206 | 3-lumen | 2.4 | 1900 | 4 | 25 | 2.8 | 0.035 | 4500 | Straight | Normal Stiff | 1 |
| RST0430NGW0206 | 3-lumen | 2.4 | 1900 | 4 | 30 | 0.035 | 4500 |
| RST0725NGW0206 | 3-lumen | 2.4 | 1900 | 7 | 25 | 0.035 | 4500 |
| RST0730NGW0206 | 3-lumen | 2.4 | 1900 | 7 | 30 | 0.035 | 4500 |
| RST0425NGW0230 | 3-lumen | 2.4 | 1900 | 4 | 25 | 0.035 | 4500 | Super Stiff |
| RST0430NGW0230 | 3-lumen | 2.4 | 1900 | 4 | 30 | 0.035 | 4500 |
| RST0725NGW0230 | 3-lumen | 2.4 | 1900 | 7 | 25 | 0.035 | 4500 |
| RST0730NGW0230 | 3-lumen | 2.4 | 1900 | 7 | 30 | 0.035 | 4500 |
Comparison Between a Rotatable Sphincterotome and a Conventional Sphincterotome
The conventional sphincterotome consists of a metal wire with insulating coating, with the distal 20–30 mm of wire exposed, and a short radio-opaque, tapered tip. Cannulation is usually attempted with a sphincterotome at present time. The conventional sphincterotome is designed to perform sphincterotomy at the 12 o'clock orientation, while a rotatable sphincterotome for ERCP in B-II patients or when cannulation/therapeutic interventions entails orientation other than the standard 11–1 o'clock position.
Benefits of Using a Rotatable Sphincterotome in Medical Procedures
1. Enhanced Precision
The Rotatable Sphincterotome offers unparalleled precision during medical procedures. Its rotatable tip allows healthcare professionals to make controlled incisions with a high degree of accuracy. This precision is particularly crucial in delicate interventions, such as sphincterotomy, where accuracy is paramount.
2. Improved Maneuverability
One of the standout advantages of the Rotatable Sphincterotome is its superior maneuverability. The rotatable tip allows for dynamic adjustments during procedures, facilitating smooth navigation through complex anatomical structures. This enhanced maneuverability is especially beneficial in endoscopic interventions where accessibility is a challenge.
3. Reduced Complication Risks
The design of the Rotatable Sphincterotome contributes to a reduction in the risk of complications during medical procedures. The precise control and flexibility provided by the rotatable tip minimize the likelihood of unintended tissue damage or other adverse outcomes. This benefit is particularly significant in interventions where minimizing complications is a primary concern.
4. Versatility in Applications
The Rotatable Sphincterotome's versatility makes it a valuable tool across various medical applications. Its adaptability in endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) procedures, including sphincterotomy for stone extraction and stent placement, underscores its utility in diverse therapeutic interventions within the hepatobiliary system.
5. Time Efficiency
Utilizing the Rotatable Sphincterotome can lead to time savings during medical procedures. The enhanced precision and maneuverability translate into a more efficient workflow for healthcare professionals. The ability to perform procedures with greater accuracy in less time is a significant advantage in a clinical setting.

 English
English 한국어
한국어 français
français Deutsch
Deutsch Español
Español русский
русский português
português العربية
العربية ไทย
ไทย