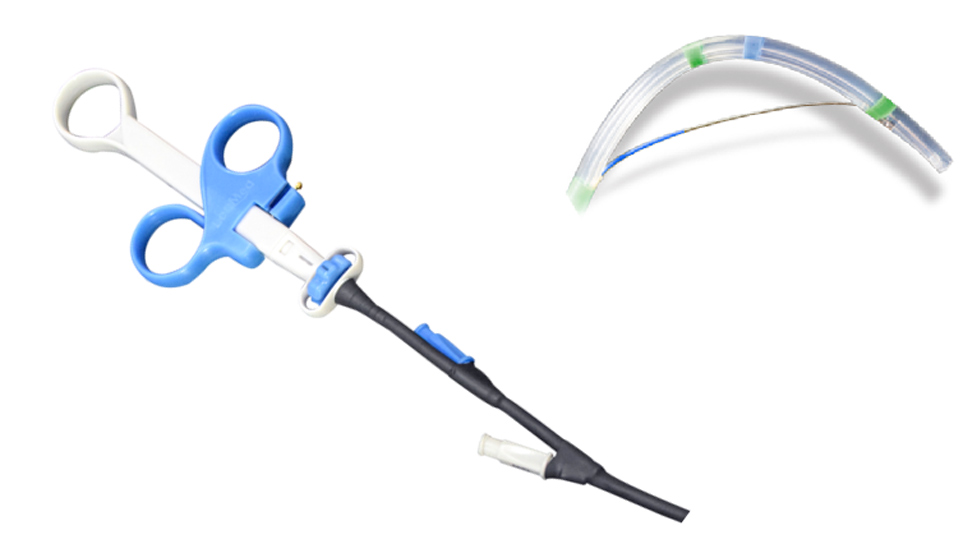
Specification of Sphincterotome ERCP
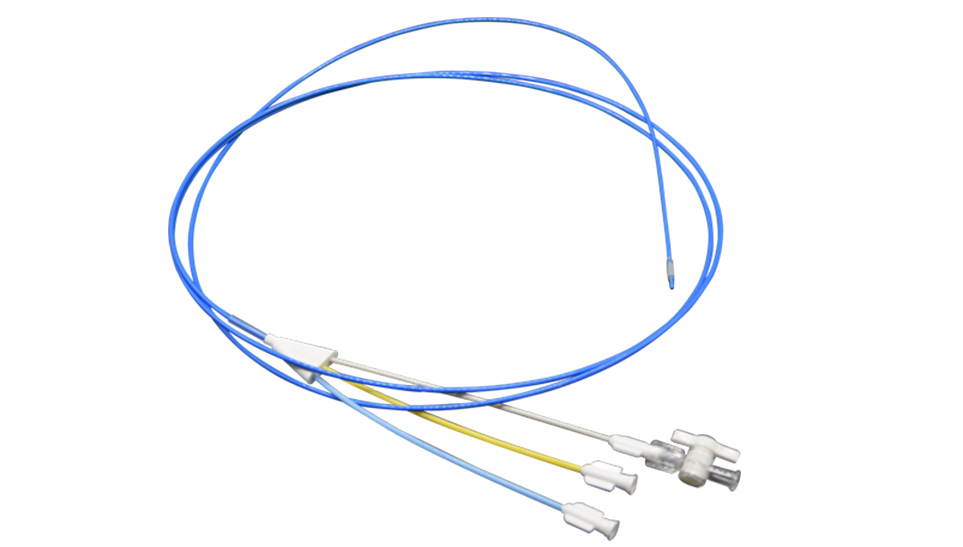
Sphincterotome (OTW)
REF
standard | Structure | Tip Length
(mm) | Cutting Length
(mm) | Working Length
(mm) | Compatible Guidewire | Minimum Working Channel (mm) | Unit/Box |
| ST0425N | 3-lumen | 4 | 25 | 1900 | 0.035 | 2.8 | 1 |
| ST0430N | 3-lumen | 4 | 30 |
| ST0725N | 3-lumen | 7 | 25 |
| ST0730N | 3-lumen | 7 | 30 |
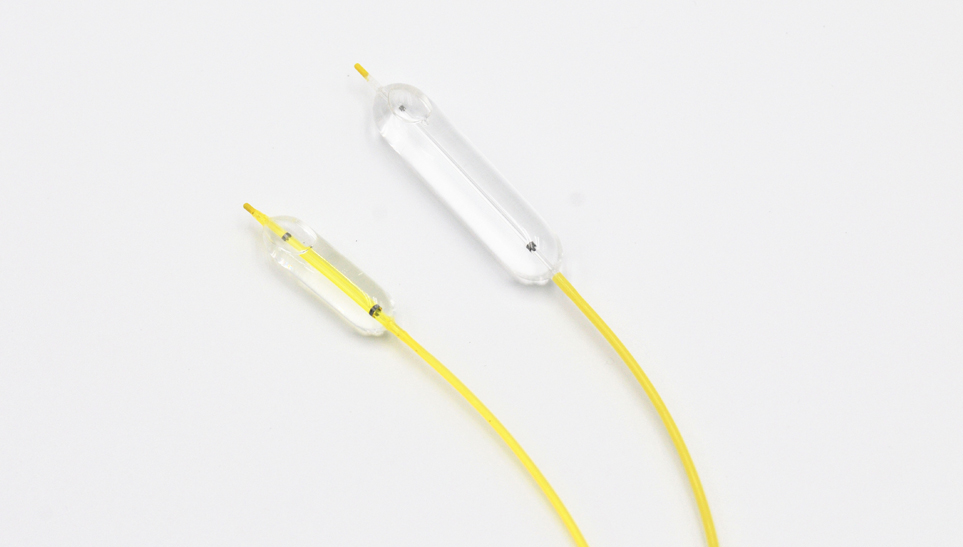
Sphincterotome (Preassembled with Guide Wire)
| REF | Structure | Catheter | Tip Length | Cutting Length | Minimum Working Channel (mm) | Guide Wire | Unit/Box |
| Standard | Outer Diam.
(mm) | Length
(mm) | (mm) | (mm) | Diam. (inch) | Length (mm) | Tip Shape | Hardness |
| ST0425NGW0206 | 3-lumen | 2.4 | 1900 | 4 | 25 | 2.8 | 0.035 | 4500 | Straight | Normal stiff | 1 |
| ST0430NGW0206 | 3-lumen | 2.4 | 1900 | 4 | 30 | 0.035 | 4500 |
| ST0725NGW0206 | 3-lumen | 2.4 | 1900 | 7 | 25 | 0.035 | 4500 |
| ST0730NGW0206 | 3-lumen | 2.4 | 1900 | 7 | 30 | 0.035 | 4500 |
| ST0425NGW0230 | 3-lumen | 2.4 | 1900 | 4 | 25 | 0.035 | 4500 | Super stiff |
| ST0430NGW0230 | 3-lumen | 2.4 | 1900 | 4 | 30 | 0.035 | 4500 |
| ST0725NGW0230 | 3-lumen | 2.4 | 1900 | 7 | 25 | 0.035 | 4500 |
| ST0730NGW0230 | 3-lumen | 2.4 | 1900 | 7 | 30 | 0.035 | 4500 |
What is a biliary endoscopic sphincterotomy?
Endoscopic Sphinctetotomy - EST,is developed on the basis of ERCP and endoscopic high frequency electroresection of digestive polyps. Since Classen (Germany) and Kawai (Japan) first carried out in 1974, this method has become a typical representative of minimally invasive treatment of digestive endoscopy.
ERCP Sphincterotomy Complications
The most frequent complications of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) and endoscopic biliary sphincterotomy are pancreatitis(4.3%), cholangitis(0.9%), hemorrhage(0.9%), and duodenal perforation(0.2%).
Endoscopic Sphincterotomy Procedure
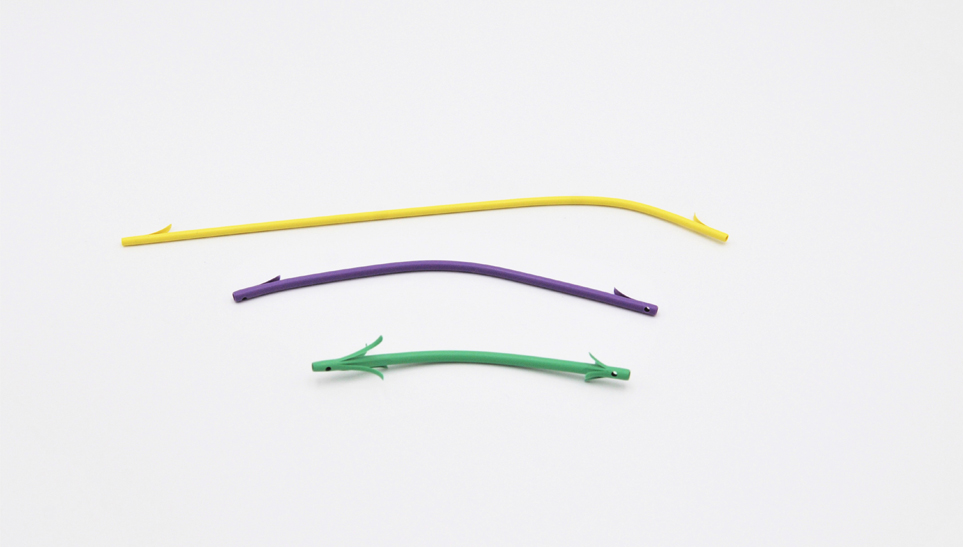
Endoscopic Sphincterotomy is performed after selective deep ductal cannulation, is regulary performed with the duodenoscope. Normally, to let the cutting wire to be forced toward the roof of the papilla, it is necessary for assistant nurse to bow the sphincterotome. To ensure the cutting wire keep its preferred angle during procedure, sphincterotome with locking mechanism is an ideal function for most nurses.
Sphincterotome Uses
A sphincterotome is a medical instrument primarily used for sphincterotomy, a procedure involving the incision of a sphincter muscle or duct. In the context of medical interventions, sphincterotomes are frequently employed in endoscopic procedures, specifically in endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP).
1. Sphincterotomy
A sphincterotome is specifically designed for sphincterotomy, which involves making controlled incisions in the sphincter muscles or ducts. This procedure is commonly performed in the biliary and pancreatic ducts during ERCP to address various medical conditions.
2. Stone Extraction
Sphincterotomes are instrumental in extracting stones from the bile or pancreatic ducts. The controlled incisions made with the sphincterotome facilitate the removal of stones, providing a therapeutic solution for patients with conditions such as choledocholithiasis.
3. Stent Placement
Another crucial application of sphincterotomes is in the placement of stents. Stents are often used to ensure the patency of ducts, and the sphincterotome facilitates the precise creation of an opening for stent insertion, contributing to the overall success of therapeutic interventions.
4. Therapeutic Interventions
Sphincterotomes play a pivotal role in various therapeutic interventions within the hepatobiliary system. These interventions may include addressing strictures, tumors, or other conditions that require precise incisions for therapeutic outcomes.
5. Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)
Sphincterotomes are integral components of ERCP procedures, where they are employed to access and treat conditions in the bile and pancreatic ducts. The use of sphincterotomes enhances the overall effectiveness of ERCP by providing healthcare professionals with a specialized tool for intricate interventions.

 English
English 한국어
한국어 français
français Deutsch
Deutsch Español
Español русский
русский português
português العربية
العربية ไทย
ไทย